- Political Engagement: This variable measures the level of active involvement and participation in political activities, such as attending political events, joining political discussions, and supporting political campaigns.
- Political Knowledge: This variable assesses the level of understanding and knowledge about political issues, processes, and actors.
- Political Participation: This variable captures the extent to which university students engage in political behaviours, including voting in elections, signing petitions, and participating in protests or demonstrations.
- The study is limited by the fact that it focuses exclusively on university students in Punjab, Pakistan. This could result in sampling bias, as the findings may not be representative of the broader population or different age groups.
- The data collected in this study rely on self-reporting through questionnaires, which can be subject to response bias. Participants may provide socially desirable answers or misrepresent their actual behaviours.
- The research is limited by its cross-sectional design, which captures data at a single point in time. Longitudinal data might provide a more comprehensive view of how memetic content influences political behaviours over time.
- The findings from this study have limited generalizability beyond the specific context of Punjab, Pakistan. Cultural, social, and political factors in other regions or countries may produce different results.
- The study may not account for all potentially confounding variables that could impact political behaviours. Factors such as prior political beliefs, family background, or exposure to traditional media may also play a role.
- Determining what constitutes "memetic content" and categorizing it accurately can be challenging. Different individuals may interpret and classify memes differently, which could introduce subjectivity into the analysis.
- Political events and social media trends are constantly changing. The timing of data collection may influence the findings, and the study may not account for important temporal dynamics.
- The ethical considerations related to the collection and analysis of online data, such as user privacy and consent, are a limitation. Additionally, ethical considerations may arise when studying political behaviours and opinions.
- The study is limited by the fact that it focuses exclusively on university students in Punjab, Pakistan. This could result in sampling bias, as the findings may not be representative of the broader population or different age groups.
- The data collected in this study rely on self-reporting through questionnaires, which can be subject to response bias. Participants may provide socially desirable answers or misrepresent their actual behaviours.
- The research is limited by its cross-sectional design, which captures data at a single point in time. Longitudinal data might provide a more comprehensive view of how memetic content influences political behaviours over time.
- The findings from this study have limited generalizability beyond the specific context of Punjab, Pakistan. Cultural, social, and political factors in other regions or countries may produce different results.
- The study may not account for all potentially confounding variables that could impact political behaviours. Factors such as prior political beliefs, family background, or exposure to traditional media may also play a role.
- Determining what constitutes "memetic content" and categorizing it accurately can be challenging. Different individuals may interpret and classify memes differently, which could introduce subjectivity into the analysis.
- Political events and social media trends are constantly changing. The timing of data collection may influence the findings, and the study may not account for important temporal dynamics.
- The ethical considerations related to the collection and analysis of online data, such as user privacy and consent, are a limitation. Additionally, ethical considerations may arise when studying political behaviours and opinions.
- Conduct longitudinal research to track changes in political behaviours and the influence of memetic content over an extended period. This would help establish causality and better understand the long-term effects.
- Expand the sample to include a more diverse demographic group, including age, socioeconomic status, and educational background. This would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of memetic content on political behaviours.
- Compare the findings with other regions or countries to assess the cultural and contextual variations in the impact of memetic content on political behaviours.
- Combine quantitative survey data with qualitative research methods like interviews or content analysis to gain deeper insights into the motivations, perceptions, and personal experiences of university students.
- Include data on actual online and offline political behaviours, such as voting patterns, attendance at political events, or engagement in political campaigns, to provide a more comprehensive view of political involvement.
- Develop a comprehensive classification system for memetic content types, themes, and contexts to better understand the variations in influence across different meme categories.
- Investigate the source and origin of memetic content, considering how the credibility of the source influences students' perceptions and actions.
- Explore the ethical implications of memetic content sharing and its potential impact on political discourse and the spread of misinformation. This can inform guidelines and recommendations for ethical meme sharing.
- Develop and evaluate education and media literacy programs for university students to enhance their critical thinking skills and ability to assess the credibility of political content, including memes.
- Encourage collaboration between researchers from various fields, such as political science, communication, psychology, and sociology, to gain a more holistic understanding of the complex relationship between memetic content and political behaviours.
- Investigate the potential policy implications of memetic content in the political sphere. This research can inform the development of guidelines and regulations related to political content on social media.
- Test the effectiveness of interventions and public awareness campaigns aimed at promoting responsible meme sharing and enhancing political awareness among university students.
- Engage with the university community and local organizations to create a more inclusive research environment and encourage active participation in political activities and discussions.
- Continue to monitor the evolving landscape of social media and memetic content to adapt research strategies to changing trends and platforms.
Abstract
This research article investigates the impact of memetic content on the political behaviours of university students in Punjab, Pakistan. With the rapid growth of social media and the increasing popularity of memetic content, understanding its influence on political behaviours becomes crucial, especially among the young and educated population. A survey-based research method has been employed, using a questionnaire as the data gathering tool, targeting university students in Punjab. The study aims to explore the relationship between exposure to memetic content and political behaviours, including political engagement, political knowledge, and political participation. The sample population consisted of university students from diverse disciplines, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of the research topic. The findings from this research will contribute to our understanding of how memetic content shapes political behaviours and may inform strategies to enhance political awareness and engagement among university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
Key Words
Memetic Content, Political Behaviours, Social Media, Political Knowledge, Memes, Social Media Influence, Media Literacy, Political Communication, Media Effects
Introduction
Social media stages have become indispensable to the lives of college understudies, advertising them as an uncommon stage for political engagement. Youthful individuals, particularly college understudies, frame a critical statistic within the social media scene, given their tall rates of web utilization and capability (Ellison et al., 2014). Their political states of mind and behaviours are affected by a few variables, including their instructive foundation, social environment, and introduction to media. Hence, media substance, counting memes, plays a significant part in forming their thought forms and political conclusions. Since memes constitute a considerable parcel of social media substance, they have a significant impact on the youth.
These days, memes have gotten to be a prevalent shape of expression, frequently combining humour, images, and content to communicate socio-political messages in a brief and outwardly engaging way. They have picked up noteworthy footing among web clients and have ended up a prevailing drive in online culture, impacting dialogues and forming open conclusions on a wide extend of themes, counting legislative issues. Memes are social artefacts that spread quickly through the web, regularly taking the frame of funny pictures, recordings, or writings that are shared and reproduced by clients. They regularly pass on a thought, concept, or feeling in a brief and regularly humorous way.
In Pakistan, where social media utilization has seen exponential development (Khan, 2019), understanding the effect of memetic substance on the political behaviours of college understudies is significant. This research points to investigate the complex relationship between introduction to memetic substance and political behaviours among college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan.
What are Memes?
The term "meme" was coined by Richard Dawkins in his 1976 book "The Childish Quality." Dawkins utilized the word to depict a thought or behaviour that spreads from individual to individual inside a culture, practically equivalent to how qualities proliferate in organic advancement. (Dawkins, 1976).
Within the setting of the web, a meme alludes to a picture, video, story, or joke that is broadly shared and circulated on the web through different implies such as e-mail, blogs, and social organizing destinations. (PC Magazine, Definition of web meme). Memes frequently contain funny or relatable substance and can spread quickly, picking up notoriety among web clients. They can take numerous shapes, counting picture macros, GIFs, recordings, or indeed textual formats.
Memes, within the shape of pictures, recordings, or literary substance, have ended up a predominant implies of communication, excitement and expression in online social orders (Lim, 2020). Thus, they have too penetrated the political circle, forming political talk and impacting open conclusions (Milner, 2016).
Memetic Substance and Political Engagement
Memes, with their imaginative and regularly funny nature, have the potential to capture consideration, inspire feelings, and spread quickly through social media stages. They can serve as effective apparatuses for political expression, permitting people to communicate their points of view in an outwardly compelling way. Memes moreover have the capacity to encourage the spread of political data, philosophies, and accounts among college understudies, possibly impacting their political states of mind and behaviours.
Social media stages such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok have gotten to be virtual battlegrounds for political talk, with memes playing an urgent part in forming the stories and talks encompassing different political issues. The availability and far-reaching utilization of these stages among college understudies make them a vital centre for considering the effect of the memetic substance on political behaviours.
Introduction to memetic substance has the potential to impact the political engagement of people. Memes regularly imbued with political messages and images, can start intrigued and engaged in political issues (Marwick & Lewis, 2017). The amusing and shareable nature of memes may persuade people to take part in discourses, share substance, and express their political sees. Past thoughts have highlighted the part of social media and online substance in forming political engagement among youth (Bekafigo & McBride, 2013; Gil de Zúñiga et al., 2012). In any case, the particular effect of the memetic substance on political engagement among college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan remains unexplored.
Memetic Substance and Political Information
The availability and virality of memetic substances have suggestions for political information procurement. Memes can streamline complex political concepts, making them more relatable and simpler to get (Bastos & Raimundo, 2018). By spreading information in a condensed and locked arrange, memes have the potential to improve political information among university understudies. In any case, the precision and profundity of data contained in memetic substances are frequently wrangled about (Ceron et al., 2016).
Memetic Substance and Political Support
Political interest, enveloping exercises such as voting, going to energizes, and locks in political discourses, could be a vital pointer of equitable citizenship (Verba et al., 1995). The impact of the memetic substance on political support among college understudies has not been broadly inspected. Memes can serve as catalysts for political discussions and mobilization, possibly empowering people to effectively take part in political exercises (Jungherr, 2016). Understanding the association between presentation to memetic substance and political interest is basic for comprehending the advancing scene of political engagement among college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan.
Issue Explanation
The quick multiplication of social media and the surge in memetic substance have on a very basic level modified the flow of political engagement among college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan. In any case, there's a hole in our understanding of how college students' utilization of memetic substance is affected by their inspirations and, in turn, how these inspirations shape their political behaviours. To address this crevice, this inquiry about points to investigate the inspirations behind college students' utilization of memetic substance and explore the relationship between these inspirations and their political behaviors, counting political engagement, political information, and political support.
Basis
This is about points to investigate the effect of memetic substances on the political behaviours of college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan. Punjab, the most crowded area in Pakistan, holds monstrous political significance, making it a perfect setting for understanding the flow between memes, social media, and political engagement among college understudies.
Past inquiries about have highlighted the part of social media in forming political behaviours and demeanours, emphasizing the impact of the online substance on individuals' recognitions and interests. In any case, this investigation will particularly centre on the effect of memetic substances on political behaviours, especially inside the setting of college understudies in Punjab.
By utilizing a survey-based inquiry about strategy, the think will examine the relationship between introduction to memetic substance and political engagement, political information, and political participation. The discoveries will shed light on the part of memetic substance in forming the political behaviours of college understudies and give profitable experiences for policymakers, teachers, and social media clients in advancing informed political talk and engagement.
Targets
1. To survey the introduction of university understudies in Punjab, to memetic substance on social media stages.
2. To look at the relationship between introduction to memetic substance and political engagement among understudies.
3. To examine the effect of memetic substance on political information levels of college understudies.
4. To analyze the impact of memetic substance on political interest and activism among students
Investigate Questions
1. To what degree are college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan exposed to memetic substances on social media stages?
2. What are the predominant sorts and topics of memetic substance that reverberate with college understudies in connection to their political behaviours?
3. How do university understudies in Punjab see the validity and dependability of memetic substances?
Speculations
H1: There's a critical relationship between introduction to memetic substance and political engagement among college understudies in Punjab, Pakistan.
H2: Memetic substance incorporates a critical effect on the political information levels of college understudies in Punjab.
H3: Memetic content significantly impacts the political support and activism of college understudies in Punjab.
Literature Review
Past thoughts have inspected the effect of social media on political engagement among youth. Bekafigo and McBride (2013) found that the presentation of political substance on social media emphatically impacted political cooperation among youthful grown-ups. Additionally, Gil de Zúñiga et al. (2012) highlighted the role of online substance in mobilizing political engagement. Memetric substance, with its humorous and shareable nature, has the potential to advance and fortify political engagement among college understudies (Marwick et al., 2017).
The openness and virality of memetic substance have suggestions for political information securing. Bastos and Raimundo (2018) recommended that memes can disentangle complex political concepts, making them more available to people. In any case, concerns have been raised with respect to the precision and depth of data contained in memes (Ceron et al., 2016). Hence, it is vital to explore how presentation to memetic content impacts political information levels among college understudies.
Humour-laced depictions of culture and web memes have invaded the computerized landscape like rapidly spreading fire. This article, titled "The Advancement of Political Memes:
Recognizing and Characterizing Web Memes with Multi-Modal Profound Learning" digs into these viral wonders, associated with advanced qualities that transform and multiply through a nonstop cycle of transformation and legacy. However, in spite of their ubiquity, small inquiries have shed light on their location and advancement online. The creators bridge this crevice by presenting "Meme-Hunter," a groundbreaking multi-modal profound learning show prepared to recognize memes from non-memes like a prepared web sleuth. This imaginative approach, surpassing the confinements of easier strategies, leverages image similarity, and meme-specific optical character acknowledgement, and confronts discovery to reveal meme families flourishing on Twitter amid the 2018 US Midterm decisions. By charting the way of meme transformation inside this pivotal discretionary setting, the consider offers compelling proof in the back of Richard Dawkins' hypothesis of meme advancement. (Beskow et al., 2020)
The web, a social dissolving pot flooding with viral patterns, has reignited the wrangle about "memes," those irresistible units of meaning passed carefully from hand to hand. In "Memes in an Advanced World:
Reconciling with a Conceptual Troublemaker," Shifman jumps headfirst into this domain, investigating how memes, long challenged indeed sometime recently the web, have blossomed beneath its glow, weaving themselves into the texture of online communication. She fastidiously weighs the merits and pitfalls of translating advanced culture through the focal point of memes. To unwind the complicated definition of what a meme genuinely is, the creator makes a system established in communication, built on three columns:
Substance, shape, and position. The notorious "Take off Britney Alone" video meme serves as a test case, exhibiting the control of this typology in activity. As the window ornament closes on this survey, Shifman paints a guide for future meme-centric investigations of the digital scene (Shifman, 2013).
Within the dynamic petri dish of YouTube, where computerized societies clash and advance, a Korean pop behemoth named "Gangnam Fashion" sparked a meme-a-palooza. The term paper "Networked Social Dissemination and Creation on YouTube:
An Investigation of YouTube Memes" jumps into this interesting marvel, investigating how YouTube served as a breeding ground for memetic imagination, with clients unleashing a torrent of spoofs, surveys, and mashups propelled by Psy's viral hit. Employing an arranged examination as their magnifying instrument, the creators looked into the perplexing web of these memetic manifestations, dismembering the ubiquity of diverse classes and the covered-up associations between them. Their discoveries disclosed "Gangnam Fashion" as a catalyst for an inventive blast, bringing forth remixes, spoofs, self-directed dance-offs, and basic audits. Besides, the investigation shed light on the fickle nature of online consideration, uncovering how a group of onlookers' engagement waxed and disappeared over the different stages of the 3-month-long memetic dissemination handle. Besides, the think about illustrates the advancing part of conventional mass media and user-generated substance in giving more extensive exposure and affirmation to viral videos over time (Xu et al., 2016).
Forget boring ads, the future of marketing lies in harnessing the infectious power of memes. A study titled "Persuasive Linguistic Tricks in Social Media Marketing Communication—The Memetic Approach" explores this fascinating concept. They propose that online content forms interconnected webs of meaning, called "memeplexes," with Persuasive Linguistic Tricks (PLTs) acting as their building blocks. Imagine, that each persuasive phrase, rhetorical question, or emotional appeal is a memetic seed, ready to sprout engagement in the fertile ground of social media. The study investigates the impact of these "seeds" by analyzing travel agency Facebook posts and user comments. They find a clear trend: positive and neutral PLTs act like growth hormones, propelling content towards viral fame. Even better, users themselves become unwitting gardeners, echoing these persuasive techniques in their responses, suggesting a self-perpetuating memetic cycle. This research offers valuable insights for marketing in the social media jungle. By understanding the memetic capabilities of PLTs, content creators can craft messages that not only resonate with emotions but also ignite user-driven amplification. The study also recommends an "evolutionary approach," recognizing how content constantly adapts and transforms within the social media ecosystem. (Stepanek et al., 2021)
When bombs fell on Gaza in May 2021, Palestinians didn't just grieve in silence. They took to TikTok, a vibrant stage for digital dances and lip-syncing, and turned it into a platform for playful activism. This article, "Playful Activism: Memetic Performances of Palestinian Resistance in TikTok #Challenges," dives into 500 videos under the hashtag #gazaunderattack, showcasing how three simple TikTok templates - lip-syncing, duets, and point-of-view - became powerful tools for resistance. Why TikTok? The study argues that this video-sharing app's playful design, built on looping snippets and playful imitation, fosters empathy and engagement in ways traditional media can't. It transforms users into co-creators, weaving together memes like threads in a tapestry of resistance. These collaborative dances, duets, and point-of-views become more than just fun - they become dialogues, rallying cries, and windows into a lived experience for a global audience.
In this digital battlefield, where playful loops morph into potent political statements, democratic engagement takes on a new form. It's no longer confined to stuffy debates or formal petitions. On TikTok, resistance becomes accessible, relatable, and tangible, a dance step at a time. This study highlights the transformative power of play, revealing how even in the face of conflict, Palestinians harnessed the creative spirit of this online space to make their voices heard, loud and clear. (Laura et al., 2023).
In the 2019 Indonesian presidential election, the battle lines weren't just drawn on rallies and billboards. They crisscrossed through the encrypted alleys of WhatsApp groups, where "meme factories" churned out digital ammunition for President Joko Widodo's re-election campaign. This study, "Memetic Persuasion and WhatsAppification," dissects this fascinating phenomenon, uncovering how political elites weaponized popular memes and exploited WhatsApp's unique features to "astroturf" public opinion. Think of these "meme factories" as secret workshops, crafting infectious visuals and catchphrases disguised as organic online chatter. WhatsApp, with its closed-door groups and cloak of encryption, became the perfect delivery channel for this digitally disguised persuasion. The study, drawing on insider interviews, sheds light on the intricate mechanics of this operation, unmasking the hidden levers that shifted public sentiment. This research adds a crucial chapter to the evolving story of WhatsApp's impact on elections globally. Beyond the usual suspects of bots and trolls, it highlights the stealthy power of "meme factories" and the hidden persuasiveness embedded within WhatsApp's technical features. In the complex digital battleground of Indonesian politics, where whispers can become roars, this study reveals how memes and messaging apps can be twisted into potent tools for shaping public opinion. (Baulch, 2022).
The research paper titled "Expression of Political Views by Young Individuals on Social Media: Exploring the Impact of Affordances and Memetic Aspects on Musical.ly" delves into the realm of political expression by young individuals on the popular app Musical.ly during the 2016 US presidential election. Employing both quantitative and qualitative content analysis on 1651 videos created by the youth, the study investigates the utilization of platform affordances, political hashtags, and memetic dimensions in conveying diverse forms of political expression. Through an examination of content, form, and stance, the research illustrates how social media serves as a platform for collective political expression among the youth, enabling intentional connections with like-minded audiences and providing a space for the exchange of symbolic resources and beliefs (Literat et al., 2019).
Top of Form
The research article "Digital Social Media and Aggression: Memetic Rhetoric in 4chan's Collective Identity" studies online aggression within digital social media, focusing on threads from 4chan's /b/board, a notorious anonymous image board known for trolling and aggressive behaviours. The author examines how some of these aggressive behaviours are memetic, meaning they are unthinking repetitions of past behaviours or perceived norms. By analyzing the technical design, ethos, and collective identity of /b/, the study sheds light on the offensive content posted on the board. It specifically looks at two threads involving transwomen, the most heavily denigrated identity on /b/, to illustrate how the collective identity's memetic responses can either fuel aggression or be disrupted through identity rhetoric to promote constructive dialogue. The case study highlights the importance of further research and pedagogy focused on anonymous and pseudonymous social media spaces to counter negative memetic behaviours and encourage more productive and democratic online discussions (Sparby, 2017).
In the tumultuous year of 2011, a wave of protests
swept across the globe, uniting hearts and screens through a new digital weapon: the protest avatar. Captured in this article, "Protest Avatars as Memetic Signifiers," is the fascinating story of how these digital symbols, from Egyptian martyrs to anonymous masks, became the battle flags of online solidarity. Unlike traditional protest symbols, these avatars weren't rigid banners; they were chameleonic memes, blurring boundaries and embracing ambiguity. This very vagueness, the author argues, fueled their viral spread across social networks, transforming avatars into rallying cries that echoed on Facebook walls and Twitter feeds. Donning these digital masks, virtual protestors found instant unity, shedding their individual identities to merge into a faceless online crowd. While this collective fusion resonated in the heat of the moment, the study raises an intriguing question: could these avatars, easily discarded like pixels on a screen, truly act as the bedrock of lasting social movements? This research delves into the intricate dance between individual and collective identity in the digital age, reminding us that while online solidarity can ignite a spark, building movements that endure may require more than just a well-chosen profile picture (Gerbaudo, 2015).
TikTok, a rapidly growing social media application, has become immensely popular among young people since its launch in 2018. Characterized by memetic videos featuring lip-syncing, dance routines, and comedic skits, TikTok has seen the rise of science memes as an increasingly popular genre. In the vibrant playground of TikTok, where dance trends reign and laughter dances on feeds, there's a quiet revolution brewing. A revolution of bubbling beakers and swirling galaxies, documented in this study, "Reposting 'till Albert Einstein is TikTok famous': The Memetic Construction of Science on TikTok." Using a digital magnifying glass, the researchers examined over 1,368 science-laced videos, tracking the viral dance of science memes through likes and shares. Their findings unveil the hidden superstars of science communication on TikTok, the clever creators weaving scientific facts into catchy loops and witty punchlines. The analysis also shines a light on the most popular topics bubbling in these memetic cauldrons, from exploding volcanoes to the mysteries of the human brain. But beyond the trending themes, the study identifies three distinct dialects of science memes on TikTok, each with its own rhythm and style. This groundbreaking research offers a treasure trove of insights for science communicators lost in the digital wilderness. It reveals the secrets of engaging the younger generation, not through dusty textbooks or droning lectures, but through the captivating language of memes. In the age of short-form attention spans and lightning-fast trends, understanding the memetic construction of science on TikTok is the key to unlocking a world of curious minds and sparking a lifelong love for science (Zeng et al., 2020).
Lost in the labyrinthine world of online memes? This paper, "Visual Semantics of Memes: (Re)Interpreting Memetic Content and Form for Information Studies," throws you a digital lifeline. It dives deep into the heart of memes, not just as funny pictures, but as complex vessels of information.
The authors propose a groundbreaking method for cracking the code of memetic meaning. They gather a vast library of memes from KnowYourMeme, a legendary meme archive, and then harness the power of Google's computer vision. By analyzing the visual features of these memes, they seek to understand how information is woven into the tapestry of their form.
Think of it like this: each meme is a puzzle piece, its image reflecting a shared "meme idea." But it's not just about identical copies. The subtle variations, and the unique twists on the image, add another layer of meaning. The study explores how this interplay between similarity and difference shapes the overall information conveyed by the meme. Their initial findings are like finding Rosetta Stones for meme enthusiasts. They suggest that analyzing these visual patterns can unlock the underlying structure of information across entire meme collections. This opens up a whole new field of research, paving the way for a deeper understanding of how information flows and evolves in the digital age. So, a meme we see, remember, it's not just a silly picture. It's a miniature message, a digital hieroglyph waiting to be deciphered. And thanks to this study, we're one step closer to untangling the fascinating language of memes (Smith et al., 2022).
Research Gap
After conducting a literature review on the topic of exploring the impact of memetic content on the political behaviours of university students in Punjab, Pakistan, several research gaps have been identified:
Limited Research in the Pakistani Context
The literature primarily focuses on Western contexts, with limited research specifically examining the impact of memetic content on political behaviours among university students in Punjab, Pakistan. This highlights a research gap in understanding the unique cultural, social, and political dynamics within Punjab, which may influence how memetic content is perceived and shared, and its ultimate impact on political behaviours.
The literature primarily focuses on Western contexts, with limited research specifically examining the impact of memetic content on political behaviours among university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
While there are studies exploring the influence of social media on political behaviours, there is a lack of research specifically targeting memetic content. Given the popularity and distinct characteristics of memes, such as their humorous and visually appealing nature, it is crucial to investigate how exposure to memetic content specifically affects the political behaviours of university students.
Insufficient Examination of Political Engagement
While some studies have explored the relationship between social media and political engagement, there is a research gap in understanding how memetic content specifically influences political engagement among university students in Punjab. Memetic content, with its viral and shareable nature, may have a unique impact on political engagement, and further research is needed to investigate this relationship.
Media Literacy and Memetric Content
The literature review reveals the importance of media literacy in navigating the digital landscape, but there is a research gap in examining the relationship between media literacy and the impact of memetic content on political behaviours among university students. Investigating the role of media literacy in critically evaluating, interpreting, and engaging with memetic content can provide valuable insights into the influence of media literacy skills on political behaviours.
Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework for this research article draws upon Uses and Gratification theory and concepts to understand the impact of memetic content on the political behaviours of university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
Uses and Gratifications Theory
The Uses and Gratifications Theory focuses on the
the active role of individuals in selecting media to fulfil their needs and desires (Katz, Blumler, & Gurevitch, 1974). University students may engage with memetic content to seek entertainment, social connection, and political information. Memes can serve as a form of political expression, allowing students to engage in discussions, share opinions, and actively participate in political discourse.
Uses & Gratification and Political Participation
According to Kruglanski et al. (2015), "Human behaviour is motivated by objectives". To explain political participation via memes, we must first understand why people are driven to utilize this medium. According to goal systems theory and appraisal theory (Lazarus, 1991), the creation and sharing of memetic content on social media platforms may be seen as a reflection of unique needs and motives, and they are "better addressed by the uses and gratification theory"(Rosengren, 1978; Lu, 2018).
Uses & Gratification and Political Knowledge
Platforms like Facebook, and Instagram have provided a place for common people, who generally don’t have access to traditional media platforms to express their viewpoints publically and get direct feedback, engage in a two-way communication, and join an online like-minded community. It allows them to act “as analysts, pundits, activists and professionals’’ (Aisar S. Musa, 2015). This enables an internet user to feel a sense of identity as he expresses his ideologies to an online community. Many people are able to engage in social networking because of their own individuality or self-status. Whiting and Williams (2013) found that 56% of their respondents expressed their ideas and thoughts on social media via liking posts, photographs, and comments. In a similar way, political memes allow people to swiftly and readily communicate their political opinions on various social media sites without much effort. So one motivation for sharing and using political memes could be to share political viewpoints and likes or dislikes towards a certain party by sharing a related meme with them.
Uses & Gratification and Political Engagement
The inclination to participate in effortful collective action is indicated by perceived political efficacy and group-related anger (Shi, Hao, Saeri, & Cui, 2015). One motivation for users to use political memes could be to engage in political participation online. The digital world has become much more real than it used to be in the past, consequently, its context and actions taken in space have become much more influential. Following the impact, people now take digital space very seriously and try to make the best use of it rather than just taking it as a medium for entertainment.
Relevance of Theory to Research Paper
The Uses and Gratifications Theory is highly relevant to the research titled "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan." Here's an analysis of its relevance:
Understanding Audience Motivations
The central focus of the Uses and Gratifications Theory is to understand why people choose specific media and what gratifications they seek. In the context of the research, this theory helps in understanding why university students in Punjab engage with memetic content on social media. By identifying the motivations behind their consumption of memetic content, the research can provide insights into what students are looking to achieve through their interactions with such content. This is crucial for understanding their behaviour in the context of political engagement.
Customization of Content
The theory emphasizes the active role of the audience in selecting and using media. University students have diverse motivations for consuming memetic content, and they often curate their social media feeds to align with their interests. This customization can significantly impact the type of political content they are exposed to and how they engage with it.
Relevance to Political Behaviors
The research aims to explore the relationship between motivations for consuming memetic content and political behaviours. Uses and Gratifications Theory provides a robust framework for linking the motivations (entertainment, information, social interaction) to political engagement, political knowledge, and political participation. It helps in understanding whether the motivations behind consuming memetic content play a role in shaping students' political attitudes and actions.
Influence of Social Media
Social media is a platform where users actively choose the content they engage with. This theory is particularly relevant in this context, as it highlights that users select media that fulfil their specific needs. Given that social media platforms are a primary source of memetic content, understanding why students choose to engage with such content is essential for comprehending the impact it has on their political behaviours.
Empowering the Audience
Uses and Gratifications Theory underscores that media consumption is an active process. It implies that individuals have agency in choosing media content that satisfies their desires. In the context of political behaviours, understanding how students actively engage with memetic content empowers them as informed consumers of political information and active participants in the political process.
In conclusion, the Uses and Gratifications Theory is highly relevant to the research on the impact of memetic content on the political behaviours of university students in Punjab, Pakistan. It helps in unravelling the motivations behind their consumption of memetic content and how these motivations are linked to their political behaviours. This theoretical framework provides a valuable lens through which to analyze the complex relationship between media consumption, motivations, and political engagement among young university students in a dynamic and evolving media landscape.
Methodology
The research design for this study is a quantitative survey-based approach. A cross-sectional design will be employed to collect data at a specific point in time, allowing for an examination of the relationship between exposure to memetic content and political behaviours among university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
Population
The population selected for this study is the University students of Punjab, Pakistan.
Sampling
The population of interest for this study will be university students in Punjab, Pakistan. A purposive sampling technique will be used to select a diverse sample of university students from different disciplines and academic levels. The sample size will be 100 university students.
Research Tool
Data is collected through a structured questionnaire.
Variables
Independent Variable
Exposure to Memetric Content: This variable refers to the extent to which university students in Punjab, Pakistan are exposed to memetic content through social media platforms and online sources. It can be measured by the frequency and duration of exposure, as well as the types of memetic content encountered (e.g., political memes, humorous political images).
Dependent Variables
Data Collection
Data will be collected through a structured questionnaire. The questionnaire has been designed to capture relevant information regarding exposure to memetic content, political engagement, political knowledge, political participation, and demographic characteristics of the participants. The questionnaire has been pilot-tested to assess its reliability and validity before the actual data collection.
Data Collection
Data will be collected through a structured questionnaire. The questionnaire has been designed to capture relevant information regarding exposure to memetic content, political engagement, political knowledge, political participation, and demographic characteristics of the participants. The questionnaire has been pilot-tested to assess its reliability and validity before the actual data collection.
Scale
Scales included in this study have a points Likert response scale, showing the rate of satisfaction of participants; starting from 1 (Strongly Agree) to 5 (Strongly Disagree).
Data Analysis
SPSS software is used for further analysis to test the hypothesis. Descriptive statistics will be employed to summarize the demographic characteristics of the participants, as well as the frequency and distribution of variables. Inferential statistics, such as correlation analysis, regression analysis, and t-tests or ANOVA, will be used to examine the relationships and associations between variables of interest.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical guidelines will be followed throughout the research process. Informed consent will be obtained from all participants, ensuring their voluntary participation and confidentiality of their responses. The study also complies with the ethical guidelines of the research institution and adheres to ethical standards for research involving human subjects.
Findings and Discussions
On inquiring about the impact of memetic content on the political behaviours of university students in Punjab, Pakistan:
Age and Gender
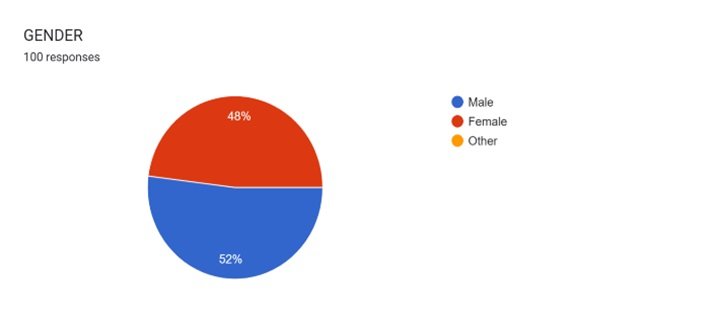
The survey was conducted among 100 participants out of which 48 female partakers and 52 male partakers responded. The survey was responded to by 52% of male respondents and 48% of female respondents.
Figure 1
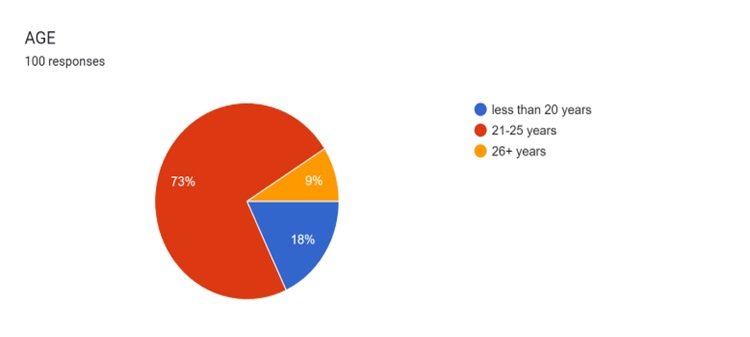
73 participants out of 100 participants belonged to the age group 21-25 (73%), while 18% belonged to the age group less than 20 years only 9% belonged to the age group greater than 26 years,
Qualification
89% of participants were full-time university students, with 70 (70%) undergraduate partakers, 12 (12%) belonged to the graduate group while 18 (18%) belonged to the post-graduate group.
The survey was taken from university students of the Punjab including the University of Education, University of Agriculture Faisalabad, University of the Punjab Lahore, UHS, Comsats Sahiwal, University of Management and Technology, Skans School of Accountancy, National Textile University, Faisalabad, PMAS Arid Agriculture University, UET Lahore, Garrison University, Gift University, Forman Christian College University, BZU Multan, UVAS Lahore, Fast Lahore and the University of Okara.
The participants are from diverse backgrounds including Mass Communication, Computer science, Textile Engineering Technology, IT, MBBS, Clinical psychology, Human nutrition and dietetics, Poultry science, BBA Marketing, Animal breeding and genetics, Animal nutrition, Islamic study, Public Health, Biochemistry, Bioinformatics, Food science and technology, Horticulture, Journalism, Mathematics, Mechatronics Engineering, Pharmacy, Botany, Accounting And Textile technology.
Social Media Usage and Political Memes
89% of participants are active social media users and use social media as a medium to get updates about political situations. 16 (16%) participants very often interact with political memes on social media platforms, 25 (25%) often interact with political memes, 23 (23%) frequently, 20 (20%) occasionally while 16 (16%) rarely interact with political memes on social media. 62 (62%) follow social media accounts or pages that primarily share political memes while 38 (38%) follow accounts or pages for political memes on social media.
Platforms for Political Memes
89% of participants are active social media users and use social media as a medium to get updates about political situations. 16 (16%) participants very often interact with political memes on social media platforms, 25 (25%) often interact with political memes, 23 (23%) frequently, 20 (20%) occasionally while 16 (16%) rarely interact with political memes on social media. 62 (62%) follow social media accounts or pages that primarily share political memes while 38 (38%) follow accounts or pages for political memes on social media.
Platforms for Political Memes
48 (48%) use Instagram accounts for political memes while 39 (39%) use Facebook and only 15 (15%) use Twitter for political memes.
Types of Memetic Content
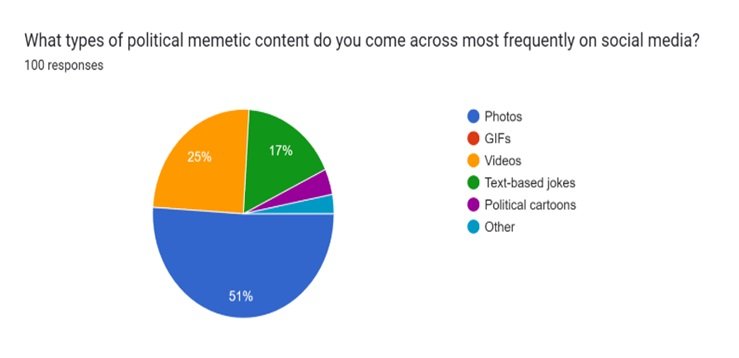
51 (51%) participants very often interact with photo-based political memes on social media platforms, 21 (21%) often interact with video political memes, 17 (17%) read text-based jokes while 4 (04%) watch political cartoons and 3 (03%) interact with other forms of political memes on social media.
Figure 3
Do you think Political Memes make you aware of Ongoing Political Events?
55 (55%) participants think political memes make them aware of ongoing political events sometimes, 19 (19%) think they frequently get political awareness by memes, 09 (9%) very frequently, 10 (10%) rarely while 07 (7%) never get political awareness by political memes.
Do you think Political Memes help you in Understanding Political ISSUES?
38 (38%) participants think political memes moderately make them aware of ongoing political events, 26 (26%) think they slightly get political understanding by political memes, 14 (14%) strongly get political awareness by political memes, 06 (6%) agree that they get political awareness very strongly, while 16 (16%) never get political awareness by political memes.
Do you Engage with Political Memes by liking, Reacting, or Commenting on them?
35 (35%) participants do not engage with political memes while 32 % rarely engage with political memes, 20 (20%) occasionally engage with political memes, 10 (10%) frequently engage with political memes, 03 (3%) very frequently political memes
Do you share the Political Memes you like?
45 (45%) participants do not share political memes while 23 (23% ) rarely share political memes, 15 (15%) occasionally share political memes, 14 (14%) often share political memes, 03 (3%) very frequently share political memes.
Do Political Memes Influence Your Political Decisions? (i.e. voting behaviour)
51 (51%) participants believe that political memes do not influence their political decisions at all, 16 (16%) participants believe that political memes rarely influence their political decisions, 20 (20%) believe that political memes sometimes influence their political decisions, 12 (12%) believe that political memes sometimes influence their political decisions frequently engage with political memes, 01 (1%) believe that political memes sometimes influence their political decisions
Have you read more about Political Events after Seeing Memes Made on Them?
34 (34%) participants believe that they rarely read about political events after seeing political memes, 27 (27%) participants believe that they occasionally read about political events after seeing political memes, 24 (24%) participants believe that they never read about political events after seeing political memes, 10 (10%) participants believe that they frequently read about political events after seeing political memes, 01 (1%) participants believe that they very frequently read about political events after seeing political memes.
How likely are you to Engage in Political Activism as a Result of Encountering Political Memetic Content on Social Media?
47 (47%) participants believe that they are neutral towards engaging in political activism as a result of encountering political memetic content on social media. 23 (23%) participants believe that they likely engage in political activism as a result of encountering political memetic content on social media. 13 (13%) participants believe that they are unlikely to engage in political activism as a result of encountering political memetic content on social media. 10 (10%) participants believe that it is very unlikely for them to engage in political activism as a result of encountering political memetic content on social media. 07 (07%)participants believe that it is very likely for them to engage in political activism as a result of encountering political memetic content on social media.
Do internet memes influence your support for any political party?
51 (51%) participants believe that internet memes never influence their support for any political party. 24 (24%) participants believe that internet memes moderately influence their support for any political party. 16 (16%) participants believe that internet memes slightly influence their support for any political party. 09 (09%) participants believe that internet memes strongly influence their support for any political party.
Do internet memes influence your opposition to any political party?
50 (50%) participants believe that internet memes do not influence their position to any political participation. 22 (22%) participants believe that internet memes moderately influence their position to any political participation. 19 (19%) participants believe that internet memes slightly influence their position in any political participation. 07 (07%) participants believe that internet memes strongly influence their position in any political participation. part. 01 (01%) participants believe that internet memes very strongly influence their position in any political participation.
What's your perception of the credibility of political memetic content on social media?
35 (35%) participants moderately perceive the credibility of political memetic content on social media. 30 (30%) participants perceive low credibility of political memetic content on social media. 18 (18%) participants somehow perceive the credibility of political memetic content on social media. 15 (15%) participants do not perceive the credibility of political memetic content on social media. 01 (01%) participants highly perceive the credibility of political memetic content on social media.
Hypotheses Testing
Hypothesis 1
H1: There is a significant relationship between exposure to memetic content and political engagement among university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
Correlation analysis was applied in SPSS Statistical Software
Confidence level of 95%
The level of significance is 0.05
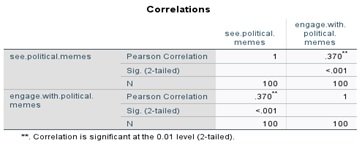


Table 1

Table2

Interpretation
The p-value is 0.370 greater than 0.05 which means the hypothesis is rejected which says that there is a significant relationship between exposure to memetic content and political engagement among university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
Hypothesis 2
H2:Memetic content has a significant impact on the political knowledge levels of university students in Punjab.
Correlation analysis was applied in SPSS Statistical Software
Confidence level of 95%
The level of significance is 0.05
Table 3
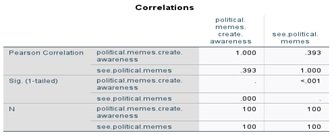
Table 4
Interpretation
The p-value is 0.393 which means the hypothesis is rejected which says that Memetic content has a significant impact on the political knowledge levels of university students in Punjab.
Hypothesis 3
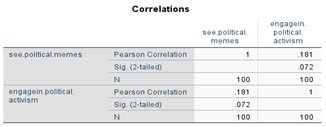
H3: Memetic content significantly influences the political participation and activism of university students in Punjab.
Correlation analysis was applied in SPSS Statistical Software
Confidence level of 95%
The level of significance is 0.05
Interpretation
The p-value is 0.072 which means the hypothesis is rejected which says that memetic content significantly influences the political participation and activism of university students in Punjab.
Discussions
Limited Impact of Memes on Political Behavior
The study reveals that memetic content has a limited role in directly influencing political engagement, knowledge, and participation among university students in Punjab, Pakistan. Despite the widespread use of memes, their impact on shaping serious political behaviours and attitudes appears to be minimal.
Memes as Initial Triggers, Not Drivers
Memes may spark initial interest in political events or topics, but they do not serve as primary drivers for deep political learning or active participation. This suggests that while memes can catch attention, they are less effective in fostering sustained political engagement or activism.
Memes may spark initial interest in political events or topics, but they do not serve as primary drivers for deep political learning or active participation. This suggests that while memes can catch a
The findings indicate a generally neutral attitude among students towards political activism, even when exposed to political memetic content. This neutrality could be influenced by various factors, including the nature of the memes themselves, which often lean towards humour and satire rather than serious political commentary.
Potential for Awareness, Not Action
While memes might not significantly influence political activism, they have the potential to raise awareness about political issues. However, this awareness does not necessarily translate into action or a deeper understanding of the political landscape.
Cultural and Contextual Factors
The study’s context within Punjab, Pakistan, suggests that cultural and regional factors may play a significant role in how memetic content is perceived and its subsequent impact on political behaviours. This highlights the importance of considering cultural nuances when examining the influence of digital media content on political attitudes and behaviours.
Conclusion
The research aimed to explore the impact of memetic content on the political behaviours of university students in Punjab, Pakistan. Through a comprehensive survey, the study gathered valuable insights from a diverse sample. The findings reveal that a significant proportion of participants perceive that political memes occasionally make them aware of ongoing political events (55%) and slightly make them understand political issues (29%). Moreover, 35% of participants do not engage with political memes, and 51% believe that political memes do not influence their support for any political party.
While these results indicate that memetic content may not be a primary driver of political awareness and engagement, it is important to note that the impact of memes on political behaviours is nuanced. The study also found that a substantial number of participants occasionally read more about political events after encountering political memes (27%). Furthermore, 47% of respondents are neutral towards engaging in political activism as a result of encountering memetic content on social media.
The perception of the credibility of political memetic content on social media varies, with 30% perceiving low credibility and 35% perceiving moderate credibility.
In conclusion, the research provides valuable insights into the complex relationship between memetic content and political behaviours among university students in Punjab, Pakistan. While a significant proportion of participants do not attribute a strong influence to memes on their political behaviours, the study highlights the potential of memetic content to spark interest and prompt further engagement with political events. The findings suggest that memes play a role in shaping political discourse, even if they may not be the sole driver of political behaviours. Understanding these dynamics is essential in the context of the ever-evolving digital landscape and its impact on political awareness and activism. As the role of memetic content in political communication continues to grow, further research is warranted to delve deeper into this dynamic interaction.
Limitations
The following are some potential limitations for a research study on "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan":
Limitations
The following are some potential limitations for a research study on "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan":
Recommendations
The following are some recommendations for a research study on "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan":
These recommendations can help guide future research efforts and provide insights into the dynamic relationship between memetic content and political behaviours among university students in Punjab, Pakistan.
References
References
-
Baulch, E., Matamoros-Fernández, A., & Suwana, F. (2022, April 14). Memetic persuasion and WhatsAppification in Indonesia’s 2019 presidential election. New Media & Society, https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448221088274
-
Beskow, D.M., Kumar, S., & Carley, K.M. (2020). The evolution of political memes: Detecting and characterizing internet memes with multi-modal deep learning. Inf. Process. Manag., 57, 102170.
Dawkins, R. (1976). The Selfish Gene. Oxford University Press. Definition of internet meme. PCMAG. (n.d.). https
-
Katz, E., Blumler, J. G., & Gurevitch, M. (1974). Utilization of Mass Communication by the Individual. In J. G. Blumler & E. Katz (Eds.), The Uses of Mass Communication: Current Perspectives on Gratifications Research (pp. 19-32). Sage
-
Literat, I., & Kligler-Vilenchik, N. (2019). Youth collective political expression on social media: The role of affordances and memetic dimensions for voicing political views. New Media & Society, 21(9), 1988–2009. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444819837571
-
Shifman, L. (2013). Memes in a Digital World: Reconciling with a conceptual troublemaker. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 18(3), 362–377.
Smith, A. O., Tacheva, J., & Hemsley, J. (2022, October). Visual Semantics of Memes: (Re) Interpreting Memetic Content and Form for Information Studies. Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 59(1), 800–802.
-
Sparby, E. (2017). Digital Social Media and Aggression: Memetic Rhetoric in 4chan’s Collective Identity. Computers and Composition. 45. 85-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compcom.2017.06.006.
-
Xu, W. W., Park, J. Y., Kim, J. Y., & Park, H. W. (2016, January 2). Networked Cultural Diffusion and Creation on YouTube: An Analysis of YouTube Memes. Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media, 60(1), 104–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/08838151.2015.1127241
-
Zeng, J., Schafer, M. & Allgaier, J. (2020). Reposting "Till Albert Einstein is TikTok famous": The Memetic Construction of Science on TikTok. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60214-2
-
Baulch, E., Matamoros-Fernández, A., & Suwana, F. (2022, April 14). Memetic persuasion and WhatsAppification in Indonesia’s 2019 presidential election. New Media & Society, https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448221088274
-
Beskow, D.M., Kumar, S., & Carley, K.M. (2020). The evolution of political memes: Detecting and characterizing internet memes with multi-modal deep learning. Inf. Process. Manag., 57, 102170.
Dawkins, R. (1976). The Selfish Gene. Oxford University Press. Definition of internet meme. PCMAG. (n.d.). https
-
Katz, E., Blumler, J. G., & Gurevitch, M. (1974). Utilization of Mass Communication by the Individual. In J. G. Blumler & E. Katz (Eds.), The Uses of Mass Communication: Current Perspectives on Gratifications Research (pp. 19-32). Sage
-
Literat, I., & Kligler-Vilenchik, N. (2019). Youth collective political expression on social media: The role of affordances and memetic dimensions for voicing political views. New Media & Society, 21(9), 1988–2009. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444819837571
-
Shifman, L. (2013). Memes in a Digital World: Reconciling with a conceptual troublemaker. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 18(3), 362–377.
Smith, A. O., Tacheva, J., & Hemsley, J. (2022, October). Visual Semantics of Memes: (Re) Interpreting Memetic Content and Form for Information Studies. Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 59(1), 800–802.
-
Sparby, E. (2017). Digital Social Media and Aggression: Memetic Rhetoric in 4chan’s Collective Identity. Computers and Composition. 45. 85-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compcom.2017.06.006.
-
Xu, W. W., Park, J. Y., Kim, J. Y., & Park, H. W. (2016, January 2). Networked Cultural Diffusion and Creation on YouTube: An Analysis of YouTube Memes. Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media, 60(1), 104–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/08838151.2015.1127241
-
Zeng, J., Schafer, M. & Allgaier, J. (2020). Reposting "Till Albert Einstein is TikTok famous": The Memetic Construction of Science on TikTok. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60214-2
Cite this article
-
APA : Amin, A., & Hussain, T. (2023). Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan. Global Multimedia Review, VI(I), 30-45. https://doi.org/10.31703/gmmr.2023(VI-I).03
-
CHICAGO : Amin, Afnan, and Tanveer Hussain. 2023. "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan." Global Multimedia Review, VI (I): 30-45 doi: 10.31703/gmmr.2023(VI-I).03
-
HARVARD : AMIN, A. & HUSSAIN, T. 2023. Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan. Global Multimedia Review, VI, 30-45.
-
MHRA : Amin, Afnan, and Tanveer Hussain. 2023. "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan." Global Multimedia Review, VI: 30-45
-
MLA : Amin, Afnan, and Tanveer Hussain. "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan." Global Multimedia Review, VI.I (2023): 30-45 Print.
-
OXFORD : Amin, Afnan and Hussain, Tanveer (2023), "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan", Global Multimedia Review, VI (I), 30-45
-
TURABIAN : Amin, Afnan, and Tanveer Hussain. "Exploring the Impact of Memetic Content on Political Behaviors of University Students in Punjab, Pakistan." Global Multimedia Review VI, no. I (2023): 30-45. https://doi.org/10.31703/gmmr.2023(VI-I).03
